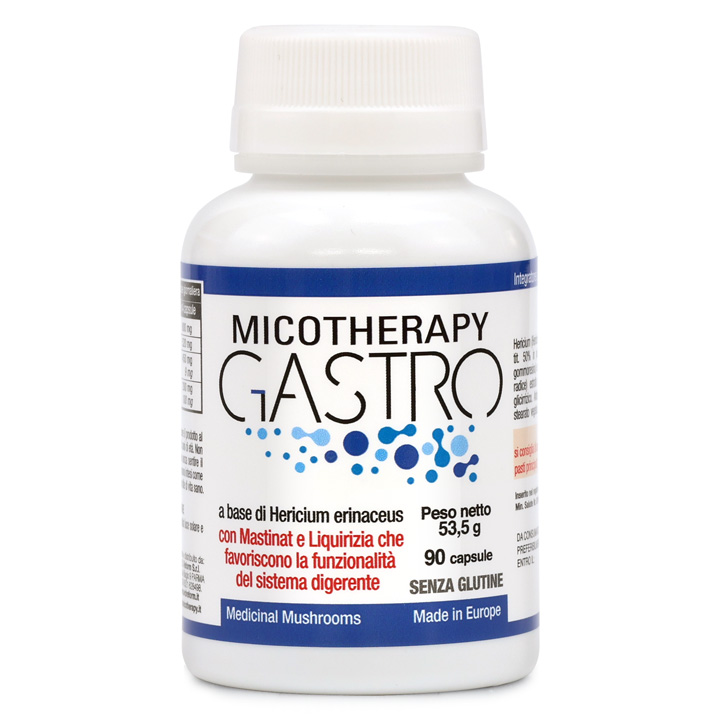
Micotherapy Hericium
Support for the nervous system and gastrointestinal system
Food supplement based on Hericium erinaceus from organic cultivation (IT BIO 006) – Made in Europe.


Properties
Also called “Lion’s mane” or “Monkey’s mushroom”, Hericium is the fungus of the digestive system and nervous system. Rich in vitamins and minerals, it was traditionally used for all gastric problems, thanks to its anti-inflammatory, healing activity and ability to regenerate the mucosa.
Obtained from organic cultivation and titrated, today it is widely studied both for its benefits on the gastrointestinal system, with direct effects on the intestinal mucosa and immune modulation, and for neurological support, and on the gut-brain axis. Studies started in 1991 have allowed to identify in Hericium erinaceus low molecular weight compounds, erinacins and ericenones, able to cross the blood-brain barrier and stimulate myelin regeneration, promoting the maintenance of normal cognitive functions.
Physiological effects
Support for the nervous system and gastrointestinal system
Ingredients
-
- Hericium erinaceus from organic farming, sporophorum and dry extract titrated in Polysaccharides, Erinacin and Ergothioneine
Contains:
- All essential amino acids
- Polysaccharides and glycoproteins
- Ericenones, Erinacin
- Triterpenes, ergosterols, bioflavonoids
- Alkaloids (Ericenine)
- Fatty acids
- Minerals: Potassium, Zinc, Iron, Germanium, Selenium, Phosphorus
- Ergothioneine
| AVERAGE CONTENT OF INGREDIENTS | PER DAILY DOSES (3 CPS) |
| Hericium sporophorum | 1200 mg |
| Hericium dry extract | 300 mg |
| Polysaccharides content | 150 mg |
| Erinacin A content | 417 mcg |
| Ergothioneine content | 346 mcg |
Instructions for use
3 capsules per day, preferably away from meals
Format
3 capsules per day, preferably away from meals
Notes
- Gluten Free
- NO GMOs
- Organic ingredients – Made in Europe
- Listed in the register of supplements: code 62492
- Paraf code: 923588990
- EAN code: 8059173430567
Bibliography
- K Nagai, A Chiba, T Nishino, T Kubota, and H Kawagishi Dilinoleoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine from Hericium erinaceum protects against ER stress-dependent Neuro2a cell death via protein kinase C pathway. J Nutr Biochem, Aug 2006; 17(8): 525-30
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Hericenones C, D, and E, stimulators of Nerve Growth Factor synthesis, from the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991; 32, 4361-4564
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Chromans, Hericenones F, G, and H from the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Phytochemistry. 1993; 32, 175-178
- Furukawa, S. et al. Biological Significance of Nerve Growth Factor and its Syntheses-Promoting Agent. Chemistry and Biology. 1991; 29. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. The Basic Chemistry of Mushrooms and Fungus and Biotechnology, Shishido, K. (editor). 2002; IPC, 212-228. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Mushroom Yearbook 2002, Efficacy of Mushrooms and its Prospectives. Plants World. 2002; 227-332. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Science of Mushrooms, Suguwara, R. (editor). Asakura Shoten. 1997; 155-180. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Search for Bioregulating Agents of Edible Mushrooms and Their Performance Analysis, Arai, S. (editor). Gakkai Shuppann Center, 1995; 37-43. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Nerve Growth Factor Synthesis-Promoting Agents, Approaches for Studying Vital Function Regulating Agents in Food. Gakkai Shuppan Center, 1996; 165-181. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Bioregulating Agents Found in Mushrooms. Food and Development. 2002; 37: 14-17. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Bioregulating Agents which Mushrooms Produce. ILSI. 2002; 70: 3-14. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. The Frontier of the Studies on Functionality of Mushrooms. Science of Food. 2002; 296: 4-12. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Bioregulating Agents which Mushrooms Produce, Kinoko-ken Dayori. 2001; 18: 5-14. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. The Secondary Metabolites of Mushrooms that Promote Synthesis of Nerve Growth Factor. Japan Mycology Journal. 2001; 42: 11-16. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Mushrooms are a Mine of Bioregulatory Agents with Unique Backbones and Functions. Chemistry and Biology. 2001; 39: 497-498. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. The Present Situation of Chemical Study on Functionality of Food. New Food Industry. 2001; 43: 25-35. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. “Good-For-Body” Agents that Edible Mushrooms Produce. Brain-Tech News. 2000; 81: 1-5. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. Mushroom-Derived Cellular Function Regulatory Agents. Agriculturization Magazine. 1994; 68: 671-677. (In Japanese)
- Kawagishi, H. et al. The Inducer of the Synthesis of Nerve Growth Factor from Lion’s Mane (Hericeum erinaceum). Explore! 2002; 11(4): 4-51
- Lee. E. W. et al. Two novel diterpenoids, erinacines H and I from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000; 64: 2402-2405
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Erinacine D, a stimulator of NGF-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Heterocycl. Commun. 1996; 2: 51-54
- Kawagishi, H. et al. Erinacines, E, F, and G, stimulators of nerve growth factor synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996; 37: 7399-7402
- The Anti-Dementia effect of Lion’s Mane mushroom and its clinical application – Hericium erinaceum – Lion’s Mane by Hirokazu Kawagishi Cun Zhuang Ellen Shnidman Townsend Letter for Doctors and Patients, April, 2004 by Hirokazu Kawagishi,Cun Zhuang, Ellen Shnidman
- Kolotushkina, E.V., M.G. Moldavan, K.Y. Voronin & G.G. Skibo, 2003. “The influence of Hericium erinaceus extract on myelination process in vitro.” Fiziologicheskii zhurnal 49(1): 38-45
- Kenmoku, H., T. Shimai, T. Toyomasu, N. Kato & T. Sassa, 2002. “Erinacine Q, a new erinacines from Hericium erinaceum, and its biosynthetic route to erinacines C in the basidiomycete.” Bioscience Biotechnology & Biochemistry Mar; 66(3)571-5
- K Mori, Y Obara, M Hirota, Y Azumi, S Kinugasa, S Inatomi, and N Nakahata Nerve growth factor-inducing activity of Hericium erinaceus in 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull, Sep 2008; 31(9): 1727-32
- K Mori, S Inatomi, K Ouchi, Y Azumi, and T Tuchida. Improving effects of the mushroom Yamabushitake (Hericium erinaceus) on mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res, Mar 2009; 23(3): 367-72
- K Ueda, M Tsujimori, S Kodani, A Chiba, M Kubo, K Masuno, A Sekiya, K Nagai, and H Kawagishi An endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-suppressive compound and its analogues from the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Bioorg Med Chem, November 1, 2008; 16(21): 9467-70
- K Ueda, M Tsujimori, S Kodani, A Chiba, M Kubo, K Masuno, A Sekiya, K Nagai, and H Kawagishi An endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-suppressive compound and its analogues from the mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Bioorg Med Chem, November 1, 2008; 16(21): 9467-70
- Moldavan MG, Grygansky AP, Kolotushkina OV, Kirchhoff B, Skibo GG, Pedarzani P. Neurotropic and Trophic Action of Lion’s Mane Mushroom Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. (Aphyllophoromycetideae) Extracts on Nerve Cells in Vitro. IntJMedMushr. Year 2007,Vol. 9 (1): 15-28
Benefits
Support for the nervous system and gastrointestinal system
In-house production cycle
We produce our supplements in our in-house laboratories to ensure performance and safety.
Useful product codes
- Entered in the register of supplements: code 62492
- Paraf Code: 983301298








Reviews