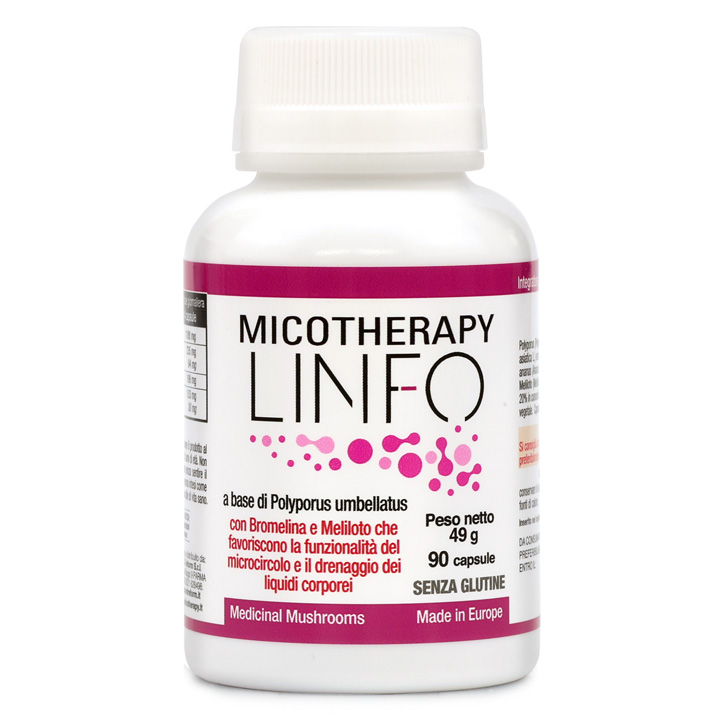
Micotherapy Linfo
Food supplement based on Polyporus umbellatus from organic farming, bromelain and plant extracts.
Properties
Based on Polyporus umbellatus from organic farming, bromelain and plant extracts, Micotherapy Linfo promotes the functionality of the microcirculation and the drainage of body fluids, counteracting situations of water retention.
The lymphatic system is made up of a complex system of vessels, very similar to the venous and arterial circulatory system. Unlike blood, lymph is not pushed by cardiac activity, but flows in the vessels thanks to movement. It extends throughout the body and originates from a thin network of lymphatic capillaries located in the extracellular space; along the path, lymph nodes appear at regular intervals, as a filtration system.
A properly functioning lymphatic system guarantees adequate “cleaning” of the extracellular matrix immersed in the interstitial fluid, in order to prevent cellular intoxication. Since the extracellular matrix is a primary bioregulation system, it is essential that it remains “clean” to ensure communication between cells, systems and organs and therefore the maintenance of the body’s homeostasis.
The remedies contained in this formulation have a strong tropism for the lymphatic and venous system, promoting the toxin drainage of the body’s tissues. They thus contribute to reducing situations of lymphatic and venous stasis, swelling, edema and water retention.
Physiological effects
Activates the lymphatic system and promotes fluid drainage.
Ingredients
- Polyporus umbellatus sporophorum
- Centella dry extract (tit. 40% in asiaticoside)
- Bromelain (tit. min. 2400 GDU/g)
- Melilotus dry extract (tit. 20% in coumarins)
- Capsule in vegetable cellulose
- Polyporus umbellatus: is a mushroom with diuretic action, which exerts its action especially in the presence of water retention, edema and difficulty urinating. Studies have shown that Polyporus does not cause side effects as it allows the elimination of sodium and chlorine but conserves potassium. Useful in the presence of lymphatic stasis
- Centella dry extract: improves venous circulation by stimulating fibroblasts, cells that regenerate collagen, a fundamental substance for the health of many tissues in the body. Useful for improving situations of peripheral venous insufficiency, cramps, hemorrhoids and cellulite
- Bromelain extracted from pineapple stems: proteolytic, antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory action. Useful for supporting mild inflammatory states of soft tissues and in the treatment of localized inflammatory conditions, particularly in the presence of edema
- Melilotus dry extract (tit. 20% in coumarins): acts on the walls of the veins, reducing their permeability and increasing capillary resistance. Improves venous return and lymphatic circulation, showing anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous activity. Useful in the presence of hemorrhoids, varicose veins, thrombophlebitis and lymphatic stasis
| AVERAGE CONTENT OF CHARACTERIZING INGREDIENTS |
PER DAILY DOSES (4 CPS) |
| Polyporus umbellatus sporophorum | 1188 mg |
| Centella dry extract | 235 mg |
| Asiatic side content | 94 mg |
| Bromelain | 198 mg |
| Melilotus dry extract | 153 mg |
| Coumarin content | 30 mg |
Instructions for use
2 capsules 2 times a day, preferably away from meals
Format
Pack of 90 capsules
Notes
Bibliography
- Yuan D, Mori J, Komatsu KI, Makino T, Kano Y. An anti-aldosteronic diuretic component (drain dampness) in Polyporus sclerotium. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 27(6):867-70
- The Pharmacological Pote ntial of Mushrooms Ulrike Lindequist, Timo H. J. Niedermeyer, and Wolf-Dieter Jülich. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med., Sep 2005; 2: 285 – 299
- Bioactivity-directed isolation, identification of diuretic compounds from Polyporus umbellatus. Zhao Y.Y, Xie R.M, Chao X, Zhang Y, Lin RC, Sun W.J. J Ethnopharmacol.2009;126(1):184-7
- Diuretic activity and kidney medulla AQP1, AQP2, AQP3, V(2)R expression of the aqueous extract of sclerotia ofsclerotia of Polyporus umbellatus FRIES in normal rats. Zhang G, Zeng X, Han L, Wei J.A, Huang H. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Epub
- Incandela L, Cesarone MR, Cacchio M, De Sanctis MT, Santavenere C, D’Auro MG, Bucci M, Belcaro G.Total triterpenic fraction of Centella asiatica in chronic venous insufficiency and in high-perfusion microangiopathy. Angiology. 2001 Oct; 52 Suppl 2:S9-13)
- (Cesarone MR, Laurora G, De Sanctis MT, Belcaro G. Activity of Centella asiatica in venous insufficiency. Minerva Cardioangiol 1992; 40: 137-43)
- Cesarone MR, Laurora G, De Sanctis MT, Incandela L, Grimaldi R, Marelli C, Belcaro G. The microcirculatory activity of Centella asiatica in venous insufficiency. A double-blind study. Minerva Cardioangiol 1994; 42: 299-304)
- Incandela L, Belcaro G, De Sanctis MT, Cesarone MR, Griffin M, Ippolito E, Bucci M, Cacchio M. Total triterpenic fraction of Centella asiatica in the treatment of venous hypertension: a clinical, prospective, randomized trial using a combined microcirculatory model. Angiology. 2001 Oct; 52 Suppl 2:S61-7)
- Incandela L, Belcaro G, De Sanctis MT, Cesarone MR, Griffin M, Ippolito E, Bucci M, Cacchio M. Total triterpenic fraction of Centella asiatica in the treatment of venous hypertension: a clinical, prospective, randomized trial using a combined microcirculatory model. Angiology. 2001 Oct; 52 Suppl 2:S61-7). • Belcaro GV, Grimaldi R, Guidi G. Improvement of capillary permeability in patients with venous hypertension after treatment with TTFCA. Angiology 1990; 41: 533-40)
- Arpaia MR, Ferrone R, Amitrano M, Nappo C, Leonardo G, del Guercio R. Effects of Centella asiatica extract on mucopolysaccharide metabolism insubjects with varicose veins. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 1990; 10: 229-33)
- Montecchio GP, Samaden A, Carbone S, Vigotti M, Siragusa S, Piovella F. Centella Asiatica Triterpenic Fraction (CATTF) reduces the number of circulating endothelial cells in subjects with post phlebitic syndrome. Haematologica 1991; 76: 256-9)
- Kim YN, Park YS, Kim HK, Jeon BC, Youn SE, Lee HY. Enhancement of the attachment on microcarriers and tPA production by fibroblast cells in a serum-free medium by the addition of the extracts of Centella asiatica. Phytotechnology 1993; 13: 221-6)
- Bonte F, Dumas M, Chaudagne C, Meybeck A. Influence of asiatic acid, madecassic acid, and asiaticoside on human collagen I synthesis. Planta Med 1994; 60: 133-5)
- Maquart FX, Bellon G, Gillery P, Wegrowski Y, Borel JP. Stimulation of collagen synthesis in fibroblast cultures by a triterpene extracted from Centella asiatica. Connect Tissue Res 1990; 24: 107-20). • Bonte F, Dumas M, Chaudagne C, Meybeck A. Comparativeactivity of asiaticoside and madecassoside on type I and III collagen synthesis by cultured human fibroblasts. Ann Pharm Fr 1995; 53: 38-42
- Walker AF, Bundy R, Hicks SM, Middleton RW. Bromelain reduces mild acute knee pain and improves well-being in a dose-dependent fashion in an open study of otherwise healthy adults. Phytomedicine 2002;9:681-6
- Taussig SJ, Batkin S. Bromelain, the enzyme complex of pineapple (Ananas comosus) and its clinical application. An update. J Ethnopharmacol 1988;22:191-203
- Stone MB, Merrick MA, Ingersoll CD, et al. Preliminary comparison of bromelain and Ibuprofen for delayed onset muscle soreness management. Clin J Sport Med 2002;12:373-8. • Nettis E, Napoli G, Ferrannini A, Tursi A. IgE-mediated allergy to bromelain. Allergy 2001;56:257-8
- Hale LP, Greer PK, Sempowski GD. Bromelain treatment alters leukocyte expression of cell surface molecules involved in cellular adhesion and activation. Clin Immunol 2002;104:183-90
- Kane S, Goldberg MJ. Use of bromelain for mild ulcerative colitis. Ann Intern Med 2000;132:680. Klein G, Kullich W. Short-term treatment of painful osteoarthritis of the knee with oral enzymes. Clin Drug Invest 2000;19:15-23
- Last JA. Hemorrhagic Sweet Clover Disease, Dicumarol, and Warfarin: the Work of Karl Paul Link. J. Biol. Chem. (2005) 280(8): e5 Kresge N, Simoni RD Hill RL. Hemorrhagic Sweet Clover Disease, Dicumarol, and Warfarin: the Work of Karl Paul Link. J. Biol. Chem. (2005) 280(8): e5
- Campbell, H. A., and Link, K. P. Studies on the Hemorrhagic Sweet Clover Disease. IV. The Isolation and Crystallization of the Hemorrhagic Agent ( 1941) J. Biol. Chem. 138, 21–33) • Stahmann, M. A., Huebner, C. F., and Link, K. P. Studies on the Hemorrhagic Sweet Clover Disease. V. Identification and Synthesis of the Hemorrhagic Agent (1941) J. Biol. Chem. 138, 513-527)
- Overman, R. S., Stahmann, M. A., Huebner, C. F., Sullivan, W. R., Spero, L., Doherty, D. G., Ikawa, M., Graf, L., Roseman, S.
- Link, K. P. Studies on the Hemorrhagic Sweet Clover Disease. XIII. Anticoagulant Activity and Structure in the 4-Hydroxycoumarin Group (1944) J. Biol. Chem. 153, 5–24
Benefits
Activates the lymphatic system and promotes fluid drainage.
In-house production cycle
We produce our supplements in our in-house laboratories to ensure performance and safety.
Useful product codes
listed in the supplement register: code 62491
Paraf code: A923582136










Reviews